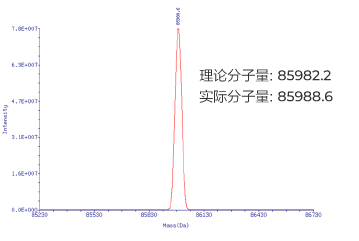
HPLC纯化的RNA (266nt):纯度高达 94.86%
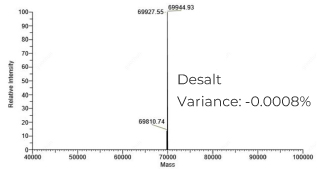
脱盐纯化的pegRNA (218nt):分子量精准
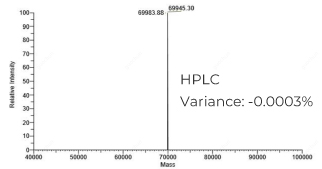
HPLC纯化的RNA (266nt):分子量精准

CRISPR/Cas9技术已发展成为基因组编辑的热门工具,它能够完成RNA导向的DNA识别及编辑,为更高效的基因编辑技术提供了全新的平台。除用于基因组编辑,CRISPR技术也应用于众多其它研究中。作为合成生物学及基因组编辑的行业领先者,金斯瑞获得美国麻省理工学院Broad研究所张锋实验室、哈佛大学和ERS Genomics授权许可,提供GenCRISPR™产品和定制服务。
CRISPR是一种来源于细菌获得性免疫的聚集空间短回文的重复序列,最初发现是在大肠杆菌(E. coli)基因组中。 CRISPR/Cas9编辑技术是由RNA指导的Cas9核酸酶对靶向基因进行编辑,只需要在细胞中导入合成的sgRNA或sgRNA表达载体,即可配合同步表达的Cas9核酸酶,对任何物种的基因组进行高效率的定向编辑。相比于ZFN系统和TALEN系统,CRISPR/Cas9是目前操作超便捷,省时、且效率足够高的基因组定点编辑技术。
基因组编辑的一站式服务
美国麻省理工学院Broad研究所、哈佛大学 和ERS Genomics授权许可
HPLC纯化的RNA (266nt):纯度高达 94.86%

脱盐纯化的pegRNA (218nt):分子量精准

HPLC纯化的RNA (266nt):分子量精准

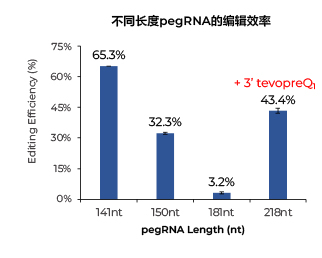
实验方法:HEK293T cells (0.2 × 106个细胞) ,电转1ug PE2/PE3 mRNA, 30pmol nicking sgRNA和90pmo不同长度的pegRNA (HPLC纯化) ,靶向HEK3位点。3天后提取基因组DNA,通过Sanger测序检测基因编辑效率。
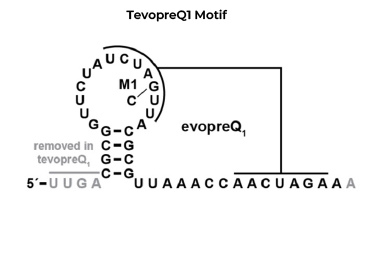
实验结果: 添加3' tevopreQ1 motif的pegRNA编辑效率可高达43.4%,远高于不加该结构的pegRNA。
备注:218nt pegRNA是181nt pegRNA添加37nt tevopreQ1 motif组成,据报道tevopreQ1 motif可以帮助pegRNA的3'端不被核酸外切酶降解。 (Nelson, J. W. et al., 2022).
欢迎使用金斯瑞sgRNA设计工具,您可以免费设计或下载序列结果,我们的工具具有以下优势:
金斯瑞为客户提供的GenCRISPR™产品和服务得到美国麻省理工学院Broad研究所、哈佛大学和ERS Genomics授权许可。GenCRISPR™产品和服务受到US 8,697,359, US 8,771,945, US 8,795,965, US 8,865,406, US 8,871,445, US 8,889,356, US 8,889,418, US 8,895,308, US 8,906,616及多国同等专利保护。
GenCRISPR™产品和该服务中生成的试剂只能作为工具用于科学研发目的,不得用于以下用途:
GenCRISPR™服务使用者和产品的购买者:
不可转让GenCRISPR™产品和该服务中生成的试剂于第三者。GenCRISPR™产品和该服务中生成的试剂只能作为工具用于科学研发目的,不得用于任何商业目的。
客户应明确知晓上述对试剂用途的限制,并自行承担因违反该限制而产生的法律责任。

李雯
华中科技大学
"我订购的主要是金斯瑞的CRISPR/Cas9系列产品,在金斯瑞合成CRISPR gRNA/Cas9 质粒以及ssDNA单链模板,使用后成功构建出稳定细胞系。在订购产品的过程中,技术支持通过电话和邮件和我沟通,及时解答我的疑惑,在订购的最终阶段,技术支持和我反复确认质粒序列是否正确,保证客户利益,值得客户信赖。感谢金斯瑞提供的优质服务。"

何燕
西湖大学
"作为一名长期致力于基因编辑研究的科研人员,我对实验中sgRNA的质量和精准度有着极高的要求。自从选择了金斯瑞的sgRNA合成服务,我惊喜地发现,他们提供的sgRNA纯度高、稳定性强,这对于确保我实验的顺利进行至关重要。使用金斯瑞的sgRNA后,我的实验效率和成功率都显著提升,让我对实验结果更有信心。我对金斯瑞的产品和服务非常满意,并会毫不犹豫地推荐其他同行选择金斯瑞作为sgRNA合成的首选合作伙伴。简而言之,金斯瑞的sgRNA合成服务,让我的科研工作更加得心应手。
